The Water Balance
The balance between inputs and outputs is known as the water balance or budget. The water balance can be shown using the formula:
precipitation (P) = streamflow (Q) + evapotranspiration (E) +/- changes in storage (S)
P=Q+E +/- S
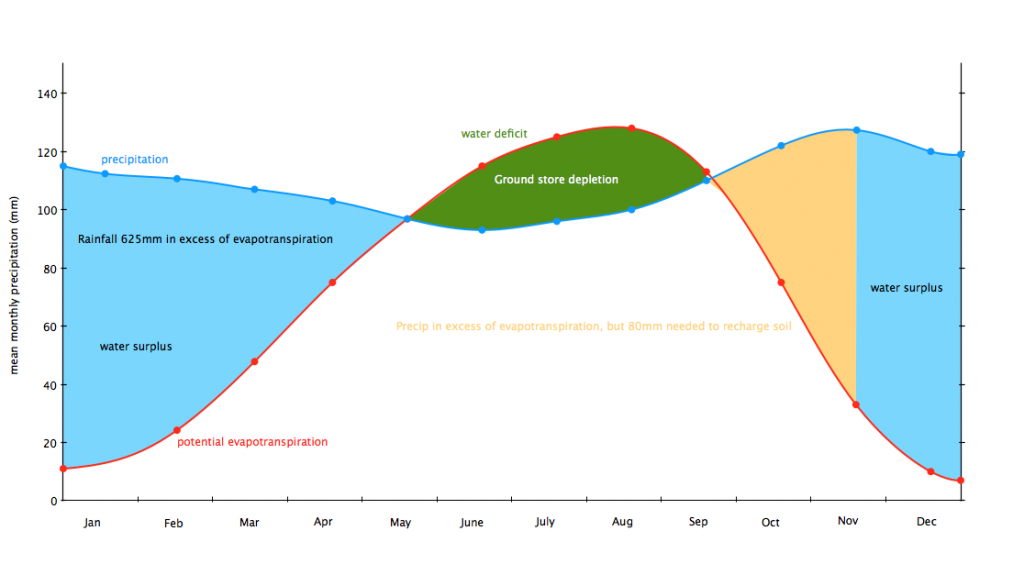
The water balance affects how much water is stored in a system. The general water balance in the UK shows seasonal patterns. In wet seasons precipitation is greater than evapotranspiration which creates a water surplus. Ground stores fill with water which results in increased surface runoff, higher discharge and higher river levels. This means there is a positive water balance. In drier seasons evapotranspiration exceeds precipitation. As plants absorb water ground stores are depleted. The is a water deficit at the end of a dry season.
Support
If you have found this site useful please support us keeping A Level Geography free by making a small, secure donation via Paypal towards to the running costs of the site.
Many thanks,
Anthony
You must be logged in to post a comment.